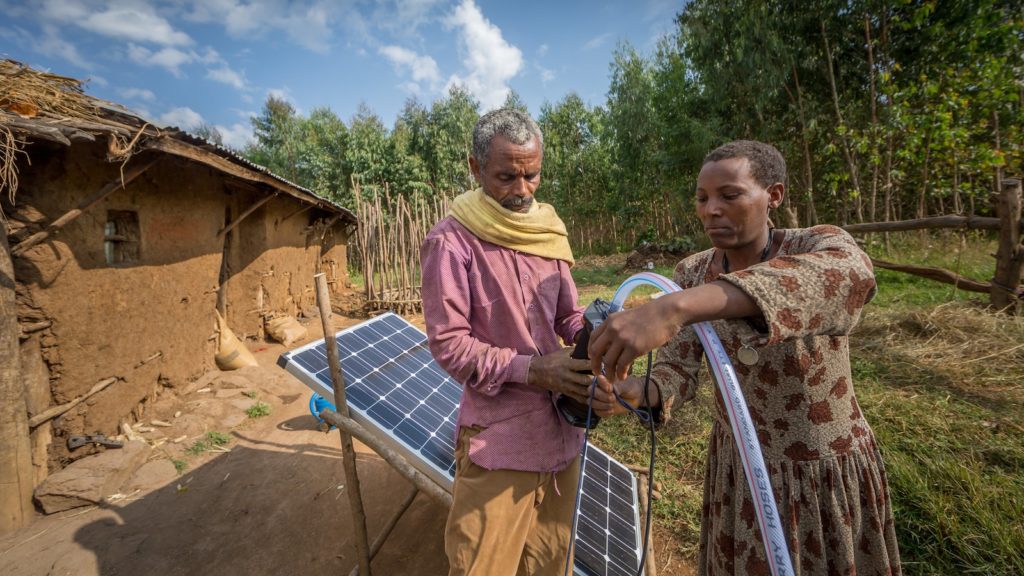
The impacts of climate change in sub-Saharan Africa are severe and have far-reaching consequences for millions of smallholder farmers. Rising temperatures, destructive locust swarms, and increasingly erratic rainfall make it difficult for farmers to grow food and meet basic needs.
Expanding small scale irrigation is emerging as part of the solution. When farmers take irrigation into their own hands, they are able to increase production, both by supplementing their rainfed crops with irrigation and by growing an additional harvest during the dry season. Small scale irrigation brings immense benefits, including better nutrition, higher incomes, and greater climate resilience.
Coming up on this year’s World Water Day, which is about water and climate change, we are taking a closer look at what it will take for even more farmers to get started with small scale irrigation.
Putting solar-powered irrigation to the (field) test
During the past few years, ILSSI and its partners, namely the International Water Management Institute (IWMI), have worked with farmers to test a number of small scale irrigation technologies. The researchers looked at how to support farmers to improve agricultural production, water use efficiency, and water productivity, and they addressed challenges related to gender inequality, lack of access to credit, and the technology supply chain.
One thing has become clear: solar-powered pumps can offer an affordable and effective irrigation solution when shallow groundwater or surface water resources are available.
Solar-powered pumps offer opportunities for farmers who are in rural areas without access to electricity. Using solar irrigation lowers costs compared to running petrol-powered pumps, and addresses other constraints related to fuels.
According to a recent report from Dalberg, “These solar water pumps have the potential to reach up to 1.6 million households in sub-Saharan Africa by 2025 and as many as 2.8 million households by 2030—a value of approximately USD 1.6 billion by 2030”. To get the best results for farmers, investments in solar-powered irrigation should be coupled with strengthening agricultural value chains, so that equipment is easily accessible in the market and produce can be off-loaded at attractive prices.
To give guidance on where solar-powered irrigation investments might best be made, IWMI researchers – partially funded by ILSSI and working as part of the CGIAR Research Program on Water, Land and Ecosystems (WLE) – developed a methodology for mapping the suitability of solar irrigation. They have now generated maps for Ethiopia, Mali, and Ghana.
During roundtable meetings organized by ILSSI, private companies have shown interest in using these maps to assess where they could grow the market, based on available resources and infrastructure. Technology supply companies have noted that they have a stake in water resource sustainability, and welcomed maps that considered agro-ecological zones, water resource availability and sustainability, as well as market factors, such as demographics and infrastructure. Companies have an interest in both economic and natural resource sustainability, but often lack the resources to individually develop such complex maps.
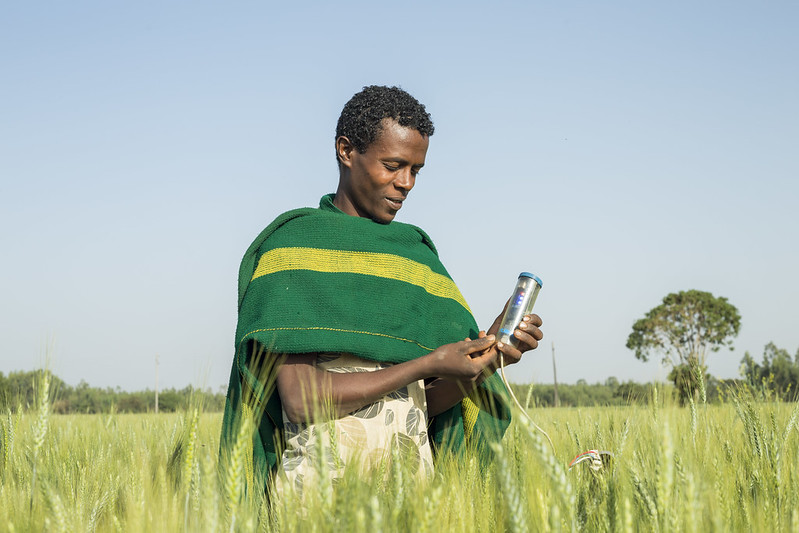

In addition to the solar suitability mapping, IWMI – through ILSSI and the Africa RISING project – have tested irrigation scheduling tools. Introduction of irrigation scheduling has enabled farmers to achieve higher water productivity. Farmers were also able to reduce their labor input by knowing when to use how much water, and that in turn meant they produced more and better crops. While the impact of using the tools varied by country, depending on capacity and information access, evidence suggested that irrigation scheduling tools have the potential to improve farmers’ income and enhance water resource management.
Expanding with the help of private sector and development partners
Two main avenues exist for expanding the use of small scale irrigation. A market-based approach seeks to strengthen the equipment supply chain and connect irrigating farmers to produce markets. Where markets are less developed, or there is a need to support resource-poor farmers, development partners and public institutions are making investments in this field.
Currently, with support from the Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ), IWMI with Futurepump and partners are scaling out the use of solar suitability maps through an online interactive tool for sub-Saharan Africa. This open access tool, currently in a test phase, can help companies determine where solar pumping would be suitable, thereby reducing the risks they might otherwise face when investing in frontier markets. The tool is currently being evaluated by private sector partners in Ghana, Ethiopia, and Mali.
The tool can also be used by development partners and NGOs to target their interventions and activities in solar-powered irrigation, and it is already in high demand. For example, GIZ found the mapping tool to be a good investment, and the Food and Agricultural Organization (FAO) is requesting national suitability analysis in West Africa to inform their regional programs.
The irrigation scheduling tools have also drawn the attention of development partners. Research under ILSSI and Africa RISING in Ethiopia suggested that farmers learn from these tools – and from each other – influencing when and how much they irrigate. These promising results have spurred other efforts. For example, a larger assessment in Ethiopia to build local communication networks for water user associations (WUA) around ICT and non-ICT based scheduling tools is funded by FAO. Along the same lines, a low-cost irrigation scheduling sensor is currently being considered for scaling in other African countries through the Water Enabler Compact under the Technologies for African Agricultural Transformation program funded by the African Development Bank.
Future efforts toward outcomes
A better understanding of barriers to and opportunities for expanding small scale irrigation is one important outcome of this ongoing research by ILSSI and its partners. These insights have informed private sector companies, donors, and development partners, which are now using ILSSI’s evidence and related tools to guide their investments in irrigation. IWMI, with the support of ILSSI and GIZ, has developed a private sector survey to further identify systemic barriers in irrigation supply chains.
Over the coming years, ILSSI will continue to help along investments in farmer-led irrigation – enabling irrigation investors to scale and expand – thus contributing to greater food production and climate resilience in sub-Saharan Africa.