by Nicole Lefore, Director of Feed the Future Innovation Lab for Small Scale Irrigation (ILSSI), Bedru Balana, Research Fellow at the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), and Claudia Ringler, Deputy Director of Environment and Production Technology Division at IFPRI
Many smallholder farmers, especially women and other marginalized groups, face difficulty in accessing loans and other forms of credit. Such credit constraints are often considered a key barrier to adoption of mechanized agricultural technologies, such as small scale irrigation equipment.
So how can this challenge be overcome? A new study indicates that the solution might be more complex than previously assumed.
A challenge with two equally important causes
In the past, both research papers and policy guidance documents have advocated for improving the supply of credit to smallholder farmers. The argument is that smallholders face credit constraints on the supply side, meaning that not enough loans or credit schemes are available to them. Therefore, the argument goes, expanding the supply of loans or other forms of finance would unleash investment in irrigation technologies.
Based on this premise, the Feed the Future Innovation Lab for Small Scale Irrigation (ILSSI) has been exploring various affordable and accessible financing options to make loans more available to small scale irrigators, to particularly address these supply-side constraints to credit.
However, a more recent ILSSI study cautions against oversimplifying the solution to credit constraints, when looking to scale irrigation technologies. It has found that demand-side factors, that is, constraints related to the farmers’ own perception and context—such as their risk aversion, bad experiences with past loans, financial illiteracy, perceived high transaction costs, and their household’s labor supply shortages—might play an equally important role, effectively shaping the amount of credit that smallholder farmers are willing to take on, even if they had access.
Complementary solutions required
Using primary data from surveys in Ethiopia and Tanzania, scientists from the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) working with ILSSI analyzed both demand- and supply-side constraints to credit. The aims of the study were to identify the credit-constraint status of smallholder farmers, that is, whether farmers are unconstrained, supply-side constrained, or demand-side constrained and to assess gender-differentiated credit constraints.
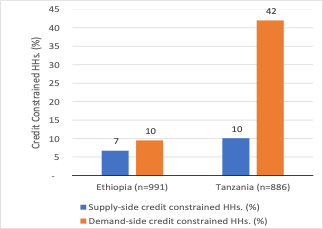
The results showed that demand-side credit constraints are at least as important as supply-side factors. The message is that easing supply-side constraints alone—for example through lowering barriers to entry for credit—will be insufficient if demand-side constraints are not also addressed. Moreover, gendered credit constraints are also on the demand side – and women face additional challenges generating demand for credit as well as accessing credit.
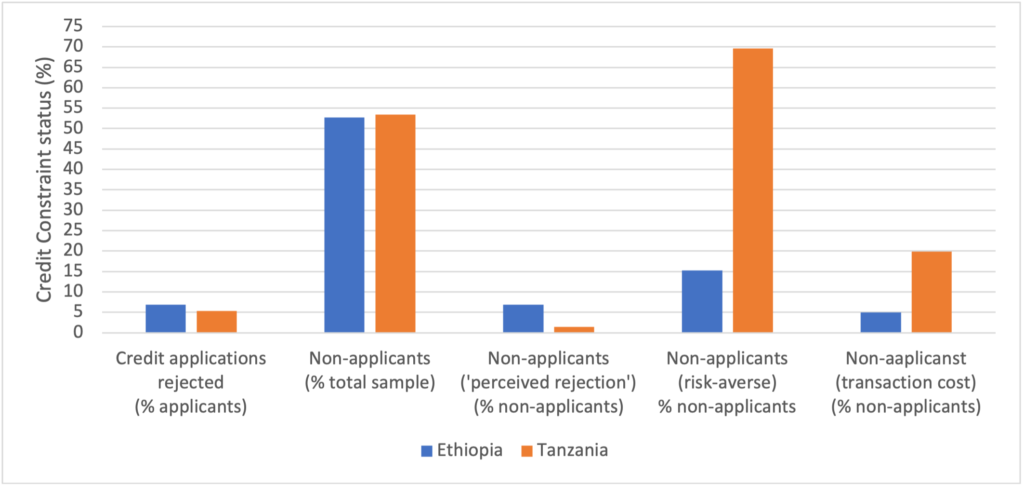
These findings open a broader discussion of what it will truly take to improve farmers’ access to and use of credit and other financing mechanisms, which can support their uptake of small scale irrigation and other technologies. As men and women farmers increasingly desire to take on irrigation, credit will continue to be critical.
Scalable solutions in finance for irrigation will require closer understanding of the nature and sources of credit constraints. What is needed is both more targeted finance instruments, from loans to asset-based finance to insurance, and complementary interventions that address demand-side constraints, such as by improving financial literacy and mitigating perceived risks. Finally, gender-sensitive credit instruments and targeted activities are needed that will both increase women’s interest in and access to credit products.
Further reading
- Are smallholder farmers credit constrained? Evidence on demand and supply constraints of credit in Ethiopia and Tanzania (IFPRI discussion paper)
- Do credit constraints affect agricultural technology adoption? Evidence from Nigeria (IFPRI project paper)
- Credit constraints and agricultural technology adoption: Evidence from Nigeria (IFPRI working paper)