by Rosaine Yegbemey, World Vegetable Center
Vegetable production in Mali has increased rapidly over the past decades. A lot of vegetable producers continue to irrigate their fields using watering cans and buckets, which is hard work and limits the scale of the operation. Nowadays, motorized water pumps including solar-powered pumps are increasingly available to Malian farmers, although adoption is still low. These pumps offer great potential to produce more, reduce drudgery, and reduce risk. However, scientific evidence is lacking on the potential benefits and costs, particularly among vegetable farmers. Such information is important to guide the scaling of the technology.
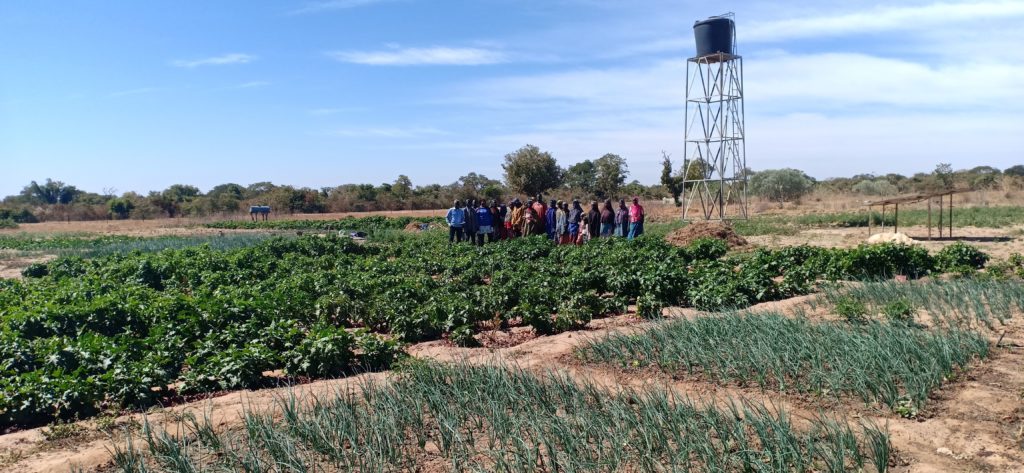

Against this backdrop and within the framework of the USAID Feed the Future Innovation Lab for Small Scale Irrigation (ILSSI), the World Vegetable Center (WorldVeg) started an evaluation study to assess the multiple impacts of solar-powered pumps in irrigated vegetable production in Mali. The study will focus on aspects of gender, cost of production, risk, household income and quality of diets.
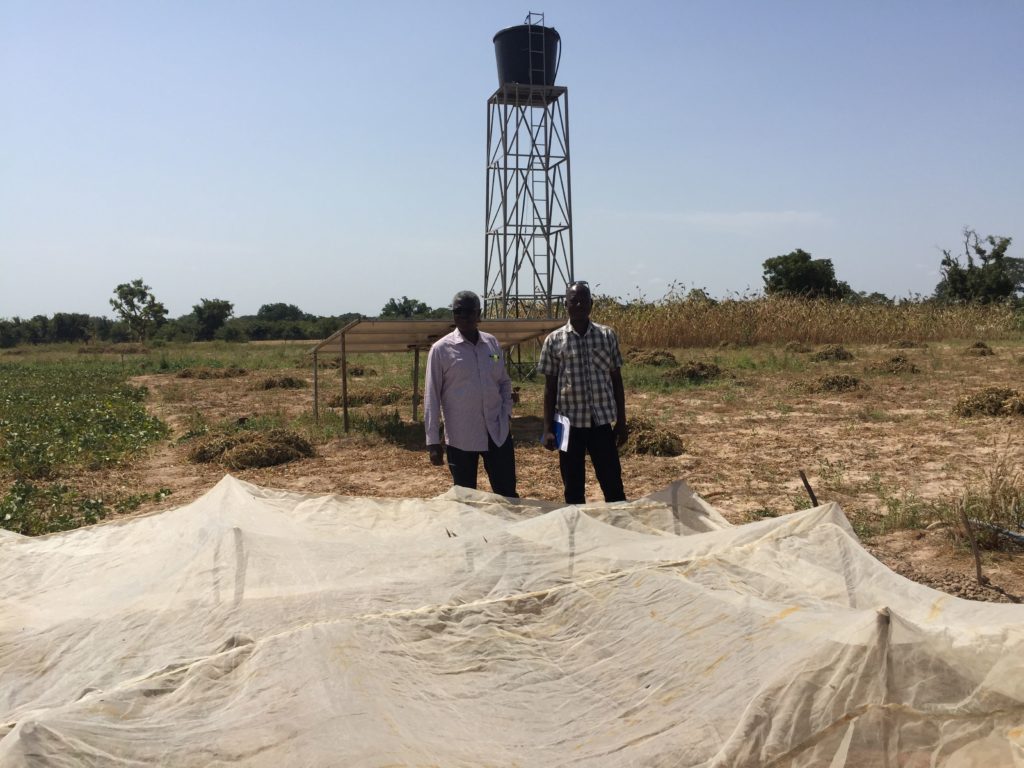
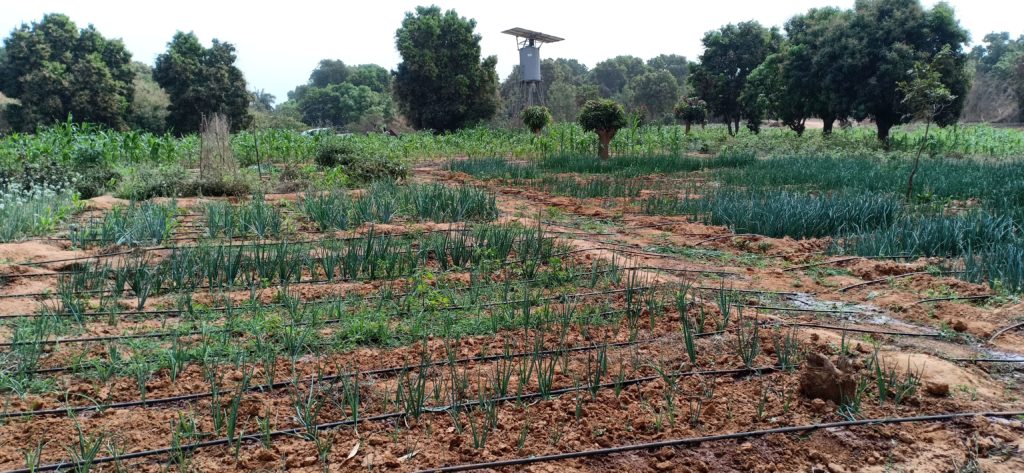


The study will use a mixed-method approach, combining quantitative and qualitative evaluation methods. Qualitative methods such as focus group discussions and in-depth personal interviews will be used to collect information from local irrigation suppliers and farmers and understand what type of farmers are adopting solar-powered pumps, as well as their experiences with the technology. Quantitative methods will rely on a farm survey of adopters and non-adopters and apply a quasi-experimental evaluation design using Propensity Score Matching (PSM). The data collection is scheduled to start in late July or early August 2022 and first results should be available toward the end of the year.